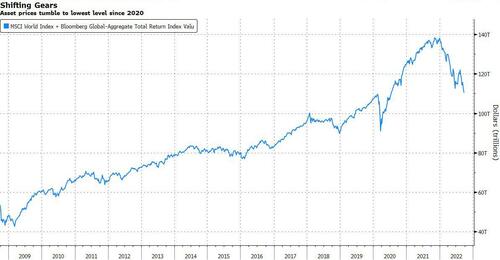
How much has the Fed's epic "inflationary is transitory" policy error cost the world? Try $29 trillion and counting.
According to calculations from Bloomberg's Robert Fullem, the combined market value of the Bloomberg Global Aggregate bond index and the MSCI World index has dropped $29 trillion since its peak in November 2021. The price gauge of the former has dropped to its lowest level since 2011. That is more than twice the level of the world's international reserves assets, currently at about $12 trillion.
As Fullem notes, the drop in asset prices may not just be about inflation or rising rates but also about the prospect of a perpetual debt spiral to fuel a modicum of growth. Central-bank rate hikes and balance sheet trimming is making future debt more expensive. In some cases, debt costs rise further amid a dearth of foreign buyers as investors stick to local markets and official accounts see reserve balances shrink. In other cases, a high absolute levels of debt and changing political landscape triggers repayment angst. Additionally, "shifting trade balances and protectionism complicates the issue as it threatens to shrink the world's production capacity and potentially turn Bernanke's global savings glut into a shortage."
Of course, the risk for central banks is that, as growth slows - and it will sharply and very soon - they will be forced to capitulate on tightening amid political concerns or domestic outrage, just as we have been warning for the past year. As a result, inflation worries will also resurface. Some of these issues may be impacting the pound and gilts, in unison.
Commenti
Posta un commento