All that may be about to change.
Speaking in a financial forum in Shangha, China's central bank governor Yi Gang said that China will keep liquidity ample in the second half of the year, but it should consider in advance the timely withdrawal of policy measures aimed at countering the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic.
"The financial support during the epidemic response period is (being) phased, we should pay attention to the hangover of the policy," Yi said. "We should consider the timely withdrawal of policy tools in advance."
In other words, just like the Fed, China is pretending that whatever is coming will be temporary. Which, in a world of helicopter money will never again be the case.
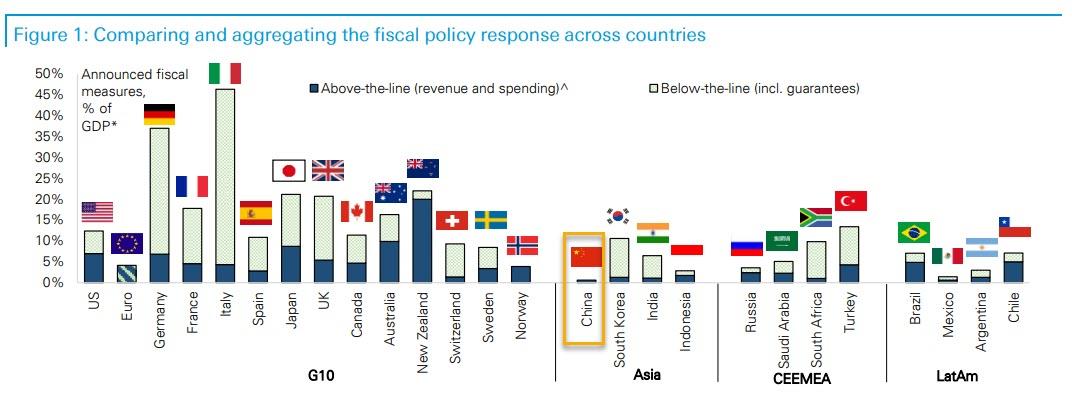
But more importantly, we know that in order to boost its stagnating economy, China is about to unleash a historic credit injection: Yi said that new loans are likely to hit nearly 20 trillion yuan ($2.83 trillion) this year, up from a record 16.81 trillion yuan in 2019, and total social financing could increase by more than 30 trillion yuan ($4.2 trillion), or about 30% of GDP. A similar number for the US would be about $7 trillion which is more or less what the US deficit will be over the next 12 months.
In other words, we're going to need a much bigger chart of China's broad credit.
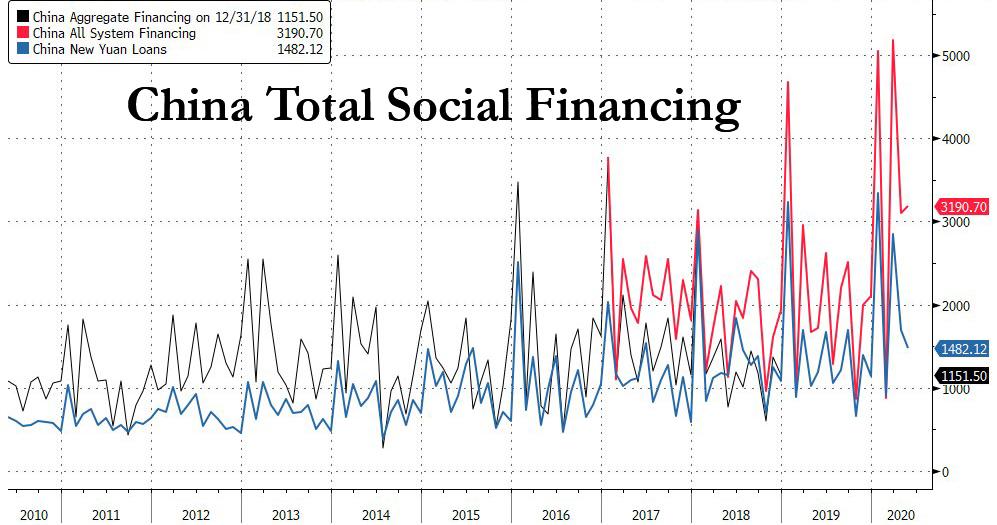
Yi added that the bank's balance sheet remains stable around 36 trillion yuan.
While the PBOC has already rolled out a raft of easing steps since early February, including cuts in reserve requirements and lending rates and targeted lending support for virus-hit firms, it has yet to proceed with a major fiscal blast. Meanwhile, analysts expect the central bank to ease policy further to bolster economy.
An in an amusing tangent, Reuters reported that Guo Shuqing, chairman of the banking and insurance regulator, told the same forum that China will not monetize fiscal deficits - in other words launch full-blown quantitative easing - and will not adopt negative interest rates. We wonder how long this promise will be kept.
It takes time for global supply chains to recover, and economies around the world have to re-think how to exit from massive easing measures that were rolled out in response to the coronavirus pandemic, said Guo.
Commenti
Posta un commento