With both 'hard' and 'soft' data showing notable weakness recently (more the surveys catching down to hard data's reality), analysts expected the latest Manufacturing survey data (for September) to show slowing growth.
- Markit's US Manufacturing PMI rose very modestly from a flash print of 60.5 to 60.7 final, but that is still down from August's 61.1 and at the lowest since April.
- ISM's Manufacturing survey rose from 59.9 to 61.1, better than the 59.5 expected – highest since May.
So take your pick – US Manufacturing at 5 month lows or 4 month highs.
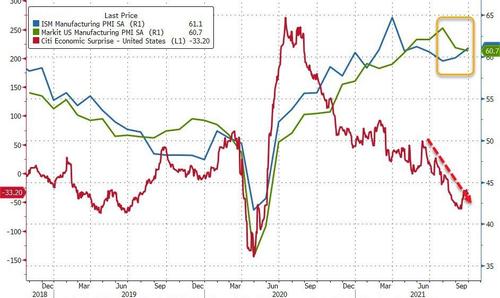
Source: Bloomberg
Stagflation fears persist as demand conditions softened from the peaks seen earlier in the year, and Markit data showed that Input costs increased at the second-fastest rate since data collection began in May 2007, easing only slightly from August's high. The sustained rise in cost burdens was linked to greater transportation charges and supplier price hikes. As a result, firms raised their selling prices at the fastest pace on record in September.Higher charges were overwhelmingly attributed to efforts to pass-through greater costs to clients.
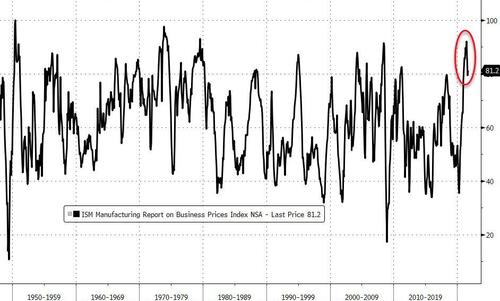
Source: Bloomberg
Chris Williamson, Chief Business Economist at IHS Markit said:
"The US manufacturing sector continues to run hot, with demand once again racing well ahead of production capacity as firms report widespread issues with supply chains and the availability of labor.
"The inability to meet demand amid near-record shortages of inputs and labor not only led to an unprecedented rise in backlogs of work as orders sat unfulfilled, but prices charged for those goods leaving the factory gate also surged higher again in September, rising at a rate exceeding anything seen in nearly 15 years of survey history.
"With COVID-19 cases showing signs of having peaked early both domestically and globally, some of the supply chain and labor shortage issues should start to ease, in turn taking some of the pressure off prices. But a dip in manufacturers' expectations for the year ahead to the lowest for four months due to supply worries underscores how production is likely to be adversely affected by shortages for some time to come."
Interestingly, hope appears to be fading too as output expectations dipped to a four-month low in September.
Commenti
Posta un commento