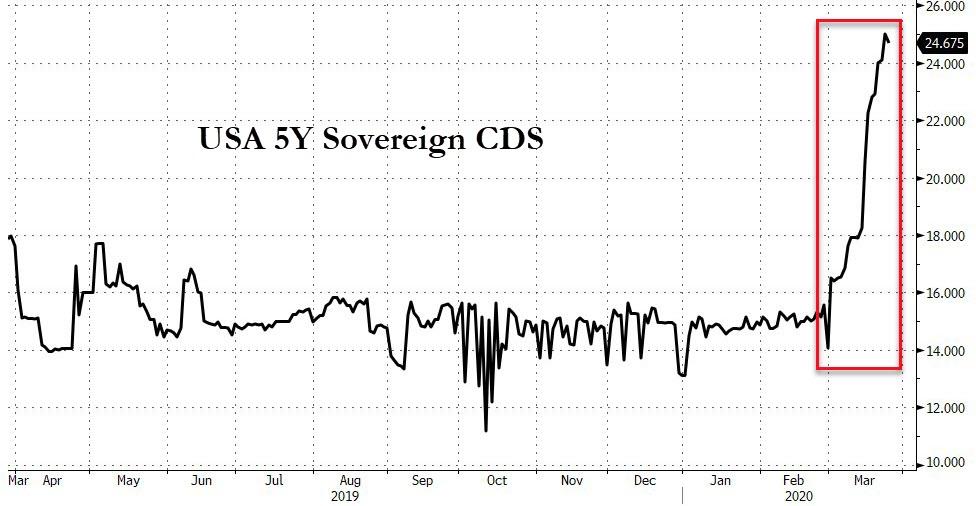
...Fitch became the first rating agency to warn that the US AAA rating was at "risk of a near-term negative action" due to a damning set of reasons including soaring debt, shrinking GDP, and the "helicopter-money" anti-virus actions.
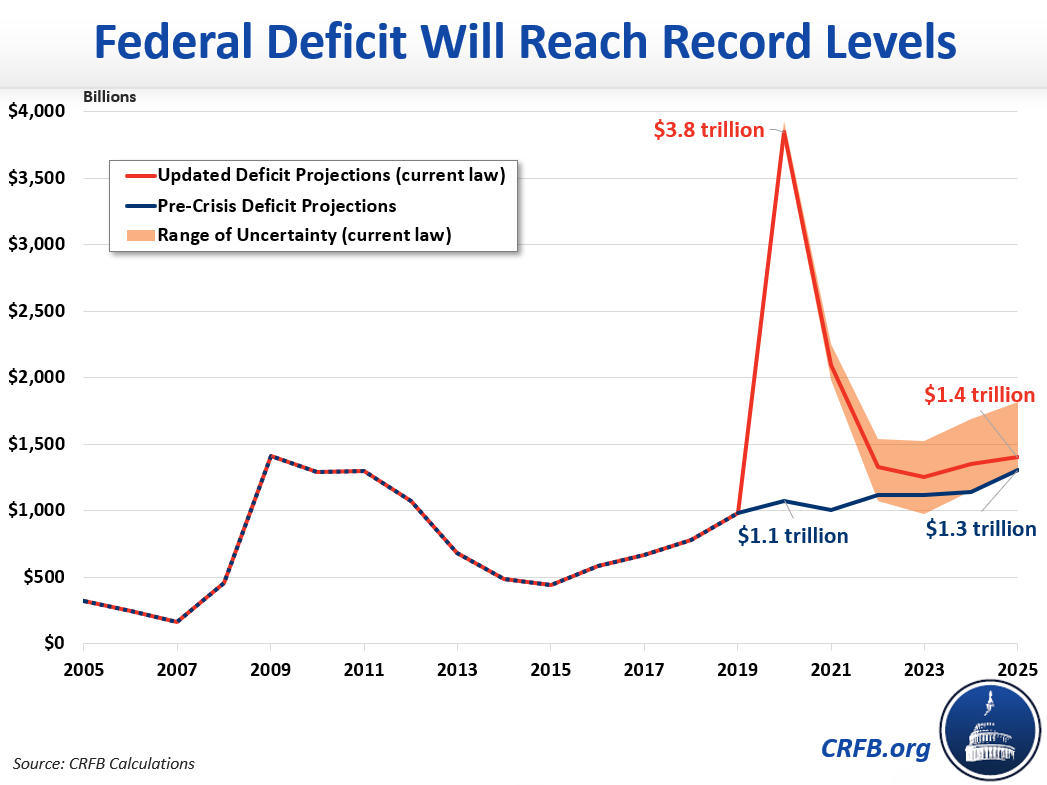
Moments ago, the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget (CRFB) issued a report which is sure to pour gasoline on that particular dumpster fire, when it projected that the US budget deficits will total more than $3.8 trillion this year, another $2.1 trillion in 2021, and will total just over $11 trillion by the end of 2025.
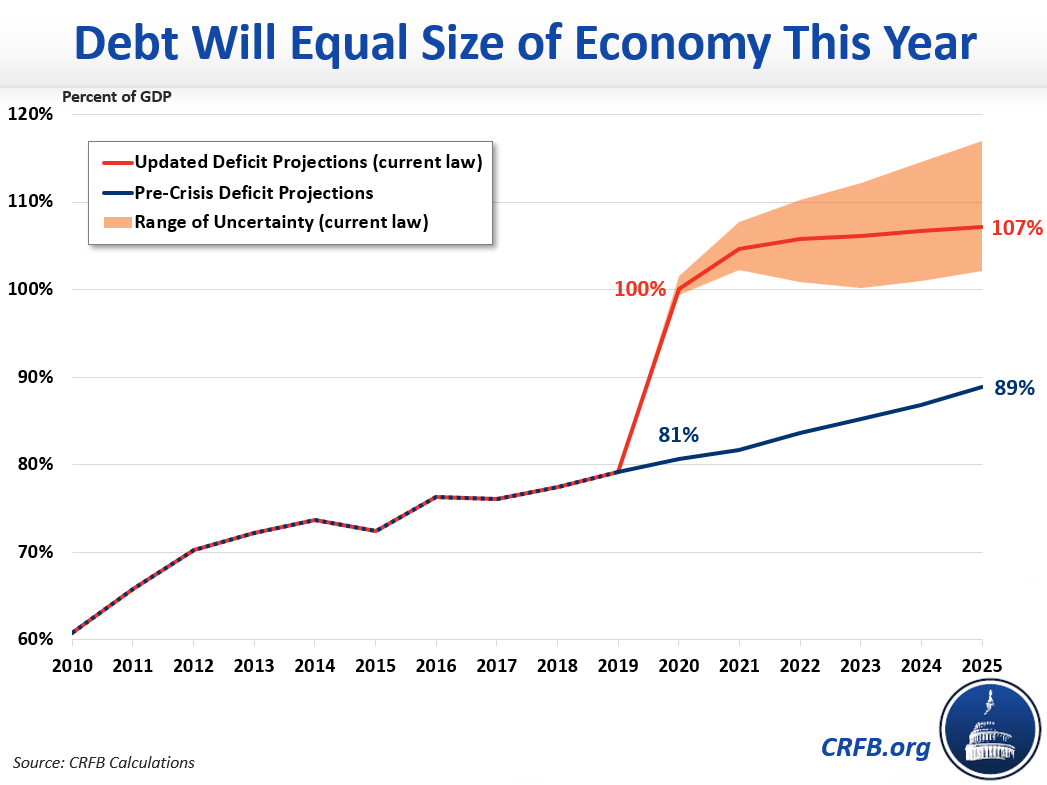
And, as we pointed out a few days ago, the CRFB now projects total debt held by the public will exceed the size of the economy, or 100% of GDP, by the end of the year, and will eclipse the record set after World War II by 2023.
* * *
In its report, the CRFB writes that the United States entered the current public health and economic crisis facing high levels of debt and trillion-dollar deficits. Due to the effects of the crisis and legislation enacted to combat it, debt and deficits will now grow much higher, to never-before-seen levels both in dollars and as a share of Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
The CRFB's latest projections find that under current law, budget deficits will total more than $3.8 trillion (18.7 percent of GDP) this year and $2.1 trillion (9.7 percent of GDP) in 2021. Meanwhile, debt held by the public will exceed the size of the economy by the end of Fiscal Year 2020 and eclipse the prior record set after World War II by 2023.
The final result will likely be even worse. As the CRFB admits, "These projections almost certainly underestimate deficits, since they assume no further legislation is enacted to address the crisis and that policymakers stick to current law when it comes to other tax and spending policies. The projections also assume the economy experiences a strong recovery in 2021 and fully returns to its pre-crisis trajectory by 2025. Assuming a slower and weaker recovery (but no changes in law), we estimate debt would grow to 117 percent of GDP by 2025."
Parroting the Fed, every politician and every recipient of bailout funds, the CRFB writes that like the record levels of borrowing undertaken during World War II, "a large share of today's massive deficits are both inevitable and necessary in light of the current pandemic crisis." As CRFB president Maya MacGuineas explained recently, "combating this public health crisis and preventing the economy from falling into a depression will require a tremendous amount of resources – and if ever there were a time to borrow those resources from the future, it is now." But just as World War II was followed by years of fiscal responsibility to restore debt to historic levels, it will be important after the crisis and recovery to ensure that debt and deficits return to more sustainable levels.
Some more from the report:
Deficits Might Quadruple This Year
Last year, the budget deficit totaled $984 billion. Under current law, we project the deficit will be nearly four times as large this year, exceeding $3.8 trillion. Our projections show the deficit will total $2.1 trillion in 2021 and roughly $1.3 trillion per year after that, through 2025. As a share of the economy, we project the deficit will total 18.7 percent of GDP in 2020, 9.7 percent in 2021, and roughly 5.6 percent per year thereafter.
By way of comparison, the previous record for nominal deficits was set in 2009, when borrowing reached $1.4 trillion. As a share of GDP, deficits never rose above 10 percent during the Great Recession. The only time deficits have ever exceeded our projection for 2020 of 18.7 percent of GDP was in a three-year span during World War II – reaching a high of 29.6 percent in 1943.
Our $3.8 trillion deficit estimate builds off of the Congressional Budget Office's (CBO) pre-crisis baseline projection of $1.1 trillion in borrowing for 2020 and its $134 billion cost estimate for the 2020 effect of the Families First Coronavirus Response Act. On top of that, we estimate the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act will cost nearly $2.1 trillion in fiscal year 2020 – though the cost could differ depending on spendout rates and amounts for various provisions, the share of loan payments that are recovered, and the budgetary treatment of certain provisions. Finally, we estimate nearly $600 billion in additional deficit spending as a result of feedback effects from lower economic output, slower inflation, higher unemployment, and lower interest rates. Our economic assumptions were generated by averaging a variety of third-party estimates and assuming economic output returns to previously projected levels by 2025.
Through 2025, we estimate deficits will total $11.3 trillion – the sum of $6.8 trillion in previously projected deficits, nearly $200 billion from the Families First Coronavirus Response Act, $2.1 trillion from the CARES Act, $1.8 trillion from economic feedback, and $350 billion from debt service. We estimate economic feedback could be as low as $900 billion or as high as $3.2 trillion under different sets of economic assumptions.
Debt Could Exceed the Size of the Economy This Year
During the Great Recession, debt grew by 21 percent of GDP between the end of 2008 and the end of 2010. Under current law, we estimate debt will grow a similar amount over just a seven month period. Specifically, we estimate debt will grow from just under 80 percent of GDP prior to the crisis to over 100 percent of GDP by the end of Fiscal Year 2020, on October 1. Our projections show debt will continue to grow as a share of GDP thereafter, exceeding the prior record of 106 percent set just after World War II by 2023 and exceeding 107 percent of GDP by 2025. The estimates assume a robust recovery in 2021 and a full recovery to pre-crisis projections by 2025.
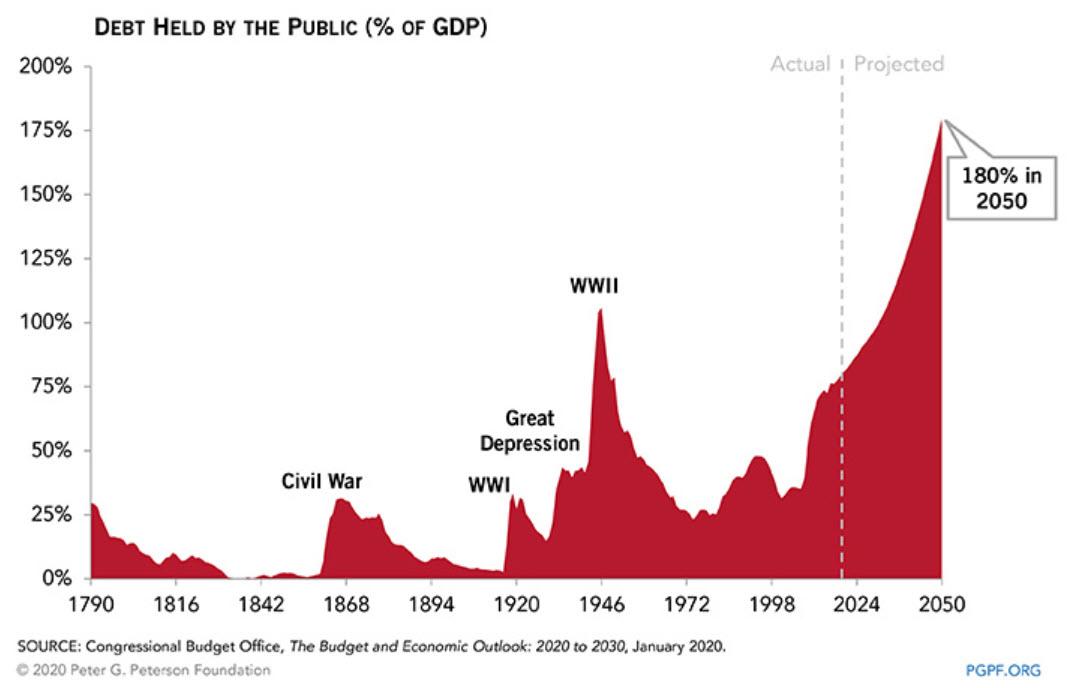
Though we have not updated our debt projections beyond 2025, the latest projections from CBO suggest debt of 107 percent of GDP in 2025 could grow to between 115 and 120 percent of GDP by 2030. This assumes large parts of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act expire after 2025.
If that wasn't bad enough, the CRFB warns that "Debt and Deficits are Likely to Be Far Higher than We Project"
Our updated debt and deficit projections are based on current law and assume a robust and ultimately full economic recovery. In theory, our projections could be too high or too low, but in reality, deficits and debt are likely to be much higher than we project.
On the economic side, we project that a faster recovery (and a full recovery of price levels) could result in deficits of $10.3 trillion through 2025 as opposed to $11.3 trillion, holding debt levels to 102 percent of GDP by 2025. On the other hand, a deeper contraction and a much slower economic recovery could result in deficits of $12.7 trillion through 2025 and debt as high as 117 percent of GDP.
Neither of these scenarios account for the (extremely likely) possibility that further legislation will be enacted to combat the current public health and economic crisis. Policymakers are already considering proposals to extend various parts of the CARES Act and pass further measures to support states, hospitals, businesses, and households. They may also enact more traditional stimulus measures once lockdowns end in an effort to jumpstart the economy.
These policies would further increase deficit and debt levels. For example, if policymakers end up spending another $1 trillion per year over the next three years on additional stimulus measures, debt as a percentage of GDP would be about 12 percentage points higher by 2025. If policymakers use the current crisis as an excuse to enact a number of permanent and unrelated policies, debt could grow even higher and larger deficits would persist in perpetuity.
At some point, such high and rising deficits and debt levels will prove unsustainable, and corrective action will be needed. Putting long-term deficit reduction measures in place sooner rather than later would allow policymakers to phase in changes more gradually and give those affected more warning and ability to prepare.
At this point someone should inform the beancounters at the CRFB about the wondrous thing called the Magic Money Tree (MMT) why explains why becoming the next Weimar Republic/Zimbabwe/Venezuela does miracles for one's fiscal outlook and confidence in the world's reserve currency.
And now we look forward to the Congressional Budget Office updating its long-term debt chart which before the Coronavirus pandemic looked like this...

Commenti
Posta un commento