So here we are late on Sunday night, with S&P futures just shy of limit down, waiting for Congress to pass a massive multi-trillion bailout legislation with Democrats and Republicans putting on a good show of sticking to their ideological talking points and roadblocking the bill's passage even though everyone knows it will pass, the only question is how much more pain will markets take before this too shall pass.
And yet, to some - such as Bank of America which was most vocal in demanding a commercial paper facility last weekend (which now seems like years ago) - not even a massive bailout package passed by Congress, one that would grant the Fed de facto powers to buy corporate bonds, will be enough.
Instead, as BofA's rates strategist Marc Cabana writes, there is "growing potential for the Fed to step up its already impressive policy response as lender of last resort." Specifically, in the coming days and weeks BofA sees a growing likelihood of:
- Adoption of UST yield curve targeting
- Full and unlimited backstop to the Agency MBS market
- Addressing regulatory constraints that have plagued intermediation of Fed repo
- Re-launch of a new TALF-like program offering senior funding on ABS, CMBS, CLOs, longer-dated munis, and investment grade corporates
- Provide guidance on the potential resolution plan for any failing entities to avoid fire sales of less liquid, riskier assets such as high yield debt, mezzanine structured product tranches, CRTs, and MSRs. Hurdles for this may prove high.
In short, BofA agrees with Zoltan Pozsar, who last week once again assessed the damage and said that the Fed will effectively have to backstop everyone and everything, in declaring a virtually total takeover of capital markets by the Fed, which is now in critical triage mode, designed to prevent further asset losses which from this point on, would have dire social and perhaps civilizations implications, potentially even the civil war that Time Magazine one mocked us for predicting back in 2010 when we said that the Fed has put the US on collision course with armed social conflict.
And so, with days, if not hours left for capital markets them before the Federal Reserve effectively takes over all risk assets, here is BofA's note urging the Fed to go all the way, which we deem is a fitting eulogy for the free markets and capitalism.
Without further ado, here is Marc Cabana's note explaining why "Bolder Fed Action is Likely", by which he means the total takover of capital markets by a group of academics who have never even held a real job in their lives:
Time to unleash the Fed's full arsenal
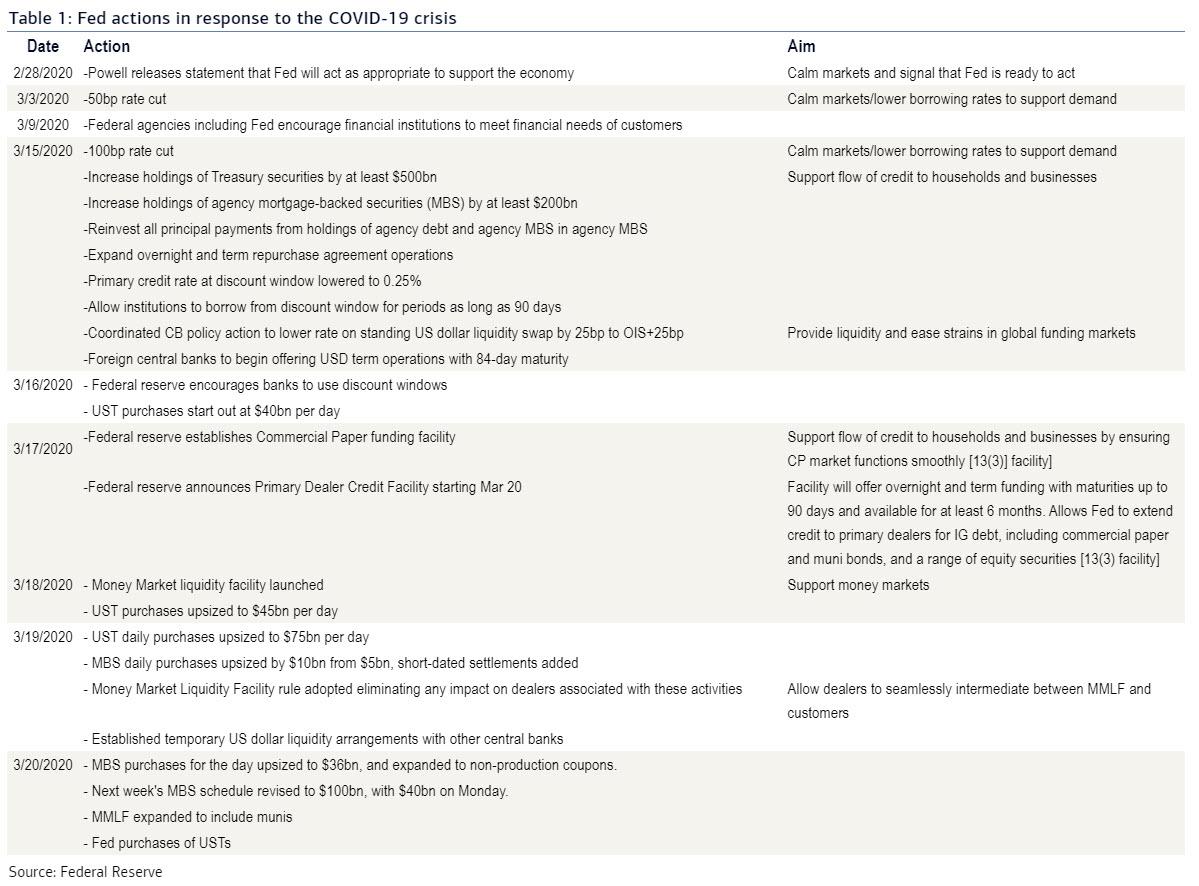
What has started out as a health care crisis has quickly spiraled into an economic one and risks quickly becoming a housing/financial crisis. The Federal Reserve has sounded the battle cry, with Chair Powell's guidance to "act as appropriate" followed by an emergency 50bp rate cut on 3 March 2020. This has been followed by quick action to meet the market's most immediate needs, in a series of steps detailed in Table 1. Scheduled asset purchases have been significantly upsized as the week progressed to stem market volatility and contain the impact of deteriorating market liquidity and forced selling.
Despite the impressive list of Fed actions last week, ongoing rate and spread volatility are amplifying the already high systemic risks:
- MBS investors who hedge rates, such as REITs, are finding themselves selling at distressed levels to fund margin calls on their rate hedges
- Fed funding for Treasuries and MBS is not being intermediated by dealers to customers
- nearly unlimited Agency and Treasury repo are effectively pushing on a string as dealer balance sheets remain constrained by regulations
- Dealers are effectively prevented from entering into a riskless transaction of passing repo on to customers as their balance sheets balloon
- Investors who fund overnight, or whose repo term matures, may find themselves forced to sell as dealer balance sheets are constrained.
To keep the situation from escalating further, and avoid the continued haphazard upsizing of daily QE purchases, we believe the Fed put needs to be made explicit, unlimited in quantity, and with a well-defined strike. To that end further "war-time" measures are needed. We believe it is time for the Fed to unleash its full arsenal to prevent these conditions worsening. We think it possible the Fed takes several additional measures in coming days or weeks, including:
Federal Reserve undertakes Yield Curve Control (YCC) by defining yield targets across the UST curve, standing ready to buy in unlimited quantities of Treasuries at those yields irrespective of settle date or off-the-run status. This can support the coming record fiscal stimulus too, although communication would need to be clear to ensure dollar reserve status is not jeopardized. We think such as measure would be very effective at reducing current Treasury illiquidity and would like only need to be temporary in nature
Just like QE1 was temporary, just like QE2 was temporary; just like QE3 was termporary; just like the QE4 bailout of repo was temporary, etc, etc, etc...
Yield targets can change over time, and the Fed would need to be sensitive to any breakeven inflation widening as signal over debt monetization controls. Fed YCC can be scaled back gradually as the markets stabilize and, we believe, will ultimately result in a smaller Fed balance sheet than the current policy. We discuss the historical precedent for this during WW2, rationale for YCC today, implementation criteria, and considerations.
Eliminate limits on Agency MBS daily purchase amount, and instead lock in MBS basis versus the yield target defined under YCC. For example the Fed could offer to buy each TBA daily at a fixed price in unlimited quantity. Prices would be published daily, with initial levels set to a reasonably wide spread, for example spot. The Fed would stand ready to buy for all settlement dates, using rolls to carry adjust as needed.
So why exactly would we need markets at this point?
With potentially unlimited purchases, dollar rolls can get squeezed if investors find themselves short bonds on TBA settle. To alleviate, the Fed would need to report daily or even intraday what they bought. Also, just like with the early days of QE3, the Fed can occasionally roll its TBA purchases forward to ensure orderly markets.
- Eliminate regulatory limits associated with riskless dealer balance sheet exposures, similar to MMLF. Regulatory limits that could be eased include cash reserves held at the Fed or repo loans secured by collateral that is pledged to, and funded by the Fed. These exposures should not count for purposes of capital or liquidity regulations, and should not count negatively toward SLR or any other ratio or stress test. We believe such regulatory relief would go a long way to address funding and liquidity issues witnessed in USTs and MBS. It would also help stabilize specified pools, which is what most MBS investors hold, giving some investors the option to fund losses rather than forcing sales, or ensuring ongoing funding for prospective buyers.
- To support liquidity in asset classes where the Fed does not offer repo, we see a growing likelihood of a substantial TALF-like facility being re-introduced. Offering non-recourse term repo that is not mark-to-market would effectively limit downside to investors with respect to potential liquidity events, and would be applicable to AAA, or at even most investment grade assets, with ratings determined as of the onset of this crisis.
This facility could face investors directly, or if #3 above is implemented, then dealers could intermediate. Asset classes could span structured products such as ABS, CMBS, CLOs, but also corporate debt and munis. Term would likely be commensurate with asset maturity, i.e. measured in years, not months. Cost and allowed leverage could be similar to TALF, or L+100, prohibitive enough to curb usage once markets stabilize.
The Fed could gear up for potential resolution planning associated with financial entity failures. The scepter of potential disorderly liquidations is impacting liquidity, creating a vicious spiral. For riskier and less liquid assets such as MSRs and CRTs not covered under the Fed repo or TALF, Maiden Lane-type facility can be created to absorb remaining illiquid assets to prevent fire-sale liquidation. Perhaps some sort of PPIP-like structure could be utilized where money managers will effectively set prices and co-invest with the government on favorable terms. Admittedly, the hurdle for this is high.
Some ass-kissing of Cabana's former employer follows, along side the hilarious admission that "post-crisis regulations to improve bank capital and liquidity were meant to ensure a repeat of 2008 would not happen. However, what is exposed now is that leverage and liquidity risk had simply shifted away from banks to other sectors of the economy and investor universe..."
The Fed has done a tremendous amount over the past 1.5 weeks but we expect there will be additional changes in coming days or weeks. Post-crisis regulations to improve bank capital and liquidity were meant to ensure a repeat of 2008 would not happen. However, what is exposed now is that leverage and liquidity risk had simply shifted away from banks to other sectors of the economy and investor universe. The corporate sector became more levered, with holdings at money managers that have quickly become sellers, as credit risk spiked and redemptions surged. mREITs, another levered sector, have been sucked into this vortex. With banks already full on liquid assets this unfortunately leaves the Fed as the only game in town, in our view.
Now if only there were those who had warned for years and years about this "totally unexpected" shifting of leverage and liquidity away from banks to the corporate sector, and instead of being mocked relentlessly by pathological permabull cretins who couldn't see the future beyond their EOD P&L, were actually listened to. Alas, that did not happen, and now taxpayers who indirectly funded all those $4 trillion in corporate buybacks over the past decade will be the same useful idiots who will be forced to double down and bailout these same "systematically important" companies like cruise lines and movie theaters.
Then, when that fails, the Fed's takeover of capital markets will go from "near-total" to "total" as the Fed starts openly buying equities to prevent the final stock market crash in one final system-saving gamble. And then, when that also fails as it has over in Japan, well that will be game over for Western civilization as we know it.
Commenti
Posta un commento