Fed Buys $587 Billion In Bonds In Past Week, 2.7% Of GDP, Just As Foreign Central Banks Start To Liquidate
This means that as of Wednesday close, when accounting for last week's repo operations, the Fed's balance sheet has increased by roughly $650BN, bringing it to just over $5.3 trillion, an increase of $1.2 trillion in the past two week, or roughly 5.6% of US GDP.
Some more scary statistics: if the Fed continues QE at the current pace of $625 billion per week, the Fed's balance sheet will hit $10 trillion by June, or just below 50% of US GDP. Even assuming the Fed eases back of the gas pedal, its balance sheet is almost certain to hit $7 trillion by June.
Which is hardly an accident: one look at the Treasury securities held in custody at the Fed shows that the past two weeks have seen a whopping $50BN in foreign central bank sales, a 1.7% drop which was the highest in six years since Russia pulled over $100BN in TSYs from the Fed in response to US sanctions imposed over the Ukraine conflict in 2014 which was precipitated by the US state department.
As Bloomberg observes, the selling may have contributed to record volatility in the Treasury market and prompted the Fed's intervention. More importantly, it also means that the biggest buyer of US Treasurys in the past decade, foreign official institutions (i.e., central banks and reserve managers) are now sellers, so now the U.S. government needs private investors to soak up the ever increasing debt issuance.
And since those are busy avoiding a deadly virus, it means that only the Fed now can fund the exploding US budget deficit... which is precisely what it is doing.
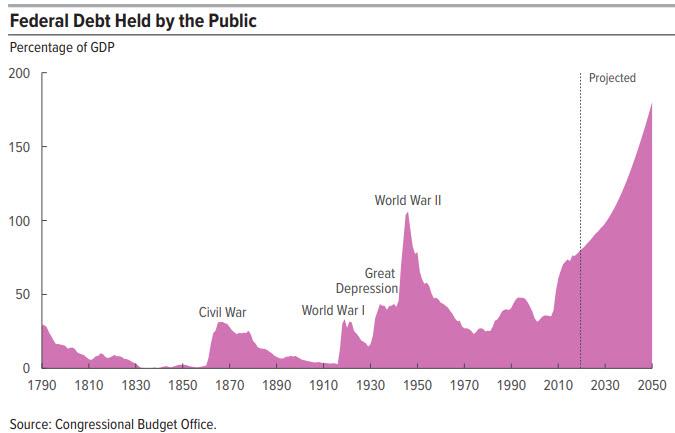
Ironically, it was back on Jan 28, just as the world was learning about the coronavirus pandemic that we showed the long-term trajectory of the Fed's balance sheet as calculated by the CBO...
... when we said that "MMT will be launched after the next financial crisis, and which will see the Fed directly monetize US debt issuance from the Treasury until the dollar finally loses its reserve currency status."
We were right about the first part. Now we just have to wait for the second.



Commenti
Posta un commento